Building on the Moon: Forecasting the Future with Today’s Tech
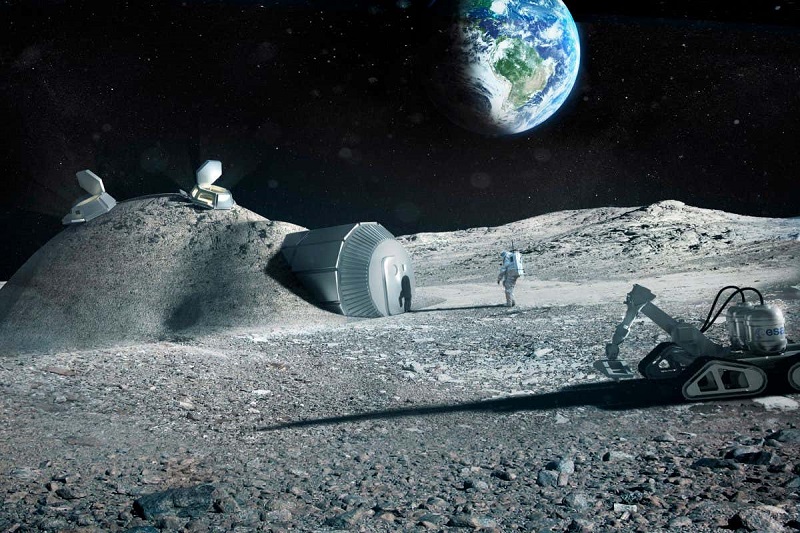

Since the dawn of space exploration, the dream of establishing a human presence on the moon has captured imaginations worldwide. Such ambitions aren’t merely confined to the realms of fiction; with advancing technologies, the concept of constructing a lunar station is inching closer to reality.
But with all the technological prowess at our disposal, what are the real prospects? How feasible is the construction of a moonbase using current tech? This article delves deep into these questions, providing an informed forecast for lunar construction in the foreseeable future.
Moonbase Essentials: What We Need
Breaking Down the Basics
To begin, constructing a moonbase requires more than just bricks and mortar. The harsh lunar environment demands a blend of innovation, resilience, and adaptability. We need materials capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, robust shielding against space radiation, and systems to produce vital resources like oxygen and water.
Fortunately, our current technological inventory offers promising solutions. With advancements in 3D printing and the discovery of water ice on the moon, we’re well on our way to crafting sustainable life-support systems and habitats.
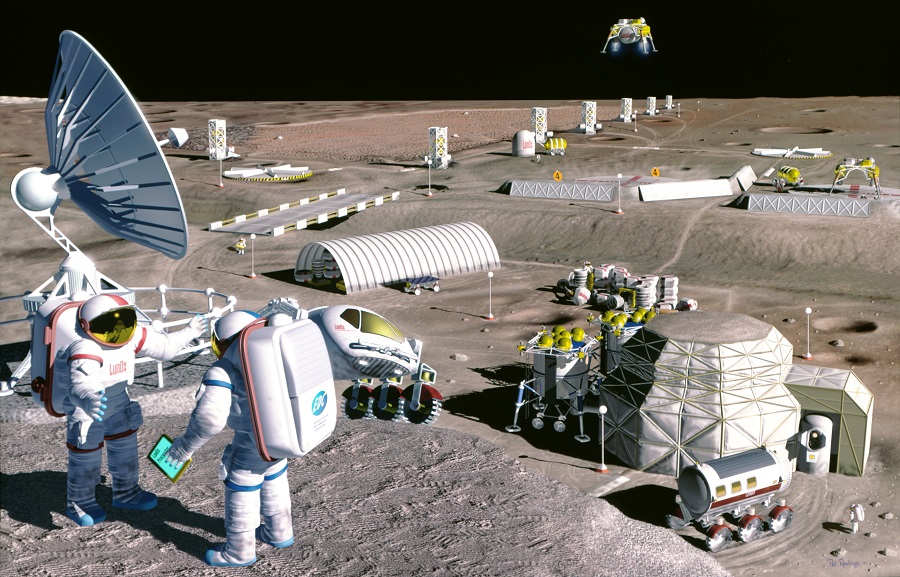
The Role of Automation and Robotics
Building Before Arrival
- Remote Construction: Modern robotics, supervised remotely from Earth, can lay the groundwork even before humans arrive, reducing risks.
- Smart Adaptability: AI-driven robots can adapt to unpredictable terrains, ensuring efficient construction under unforeseen circumstances.
- Resource Utilization: Robots equipped with the right tools can extract and process lunar materials, cutting down the need to transport vast amounts of resources from Earth.
- Safety Protocols: Automation can handle tasks deemed too risky for humans, such as tunneling or dealing with potential lunar quakes.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Post-construction, robots can play an essential role in maintaining and upgrading the lunar station, ensuring longevity.
Lunar Construction Challenges
While our toolkit is impressive, several challenges lie ahead. The absence of a lunar atmosphere means direct exposure to harmful cosmic and solar radiation. Lunar dust, fine and abrasive, poses a risk to both equipment and astronauts. Additionally, the communication delay between the moon and Earth, although only slight, can complicate remote operations.
Overcoming these challenges necessitates innovative materials and construction techniques. For instance, creating habitats beneath the lunar surface or using lunar regolith as a radiation shield are potential solutions being explored.
International Collaborations: Key to Success
The enormity of constructing a station on the moon surpasses the capabilities of any single nation. International collaborations, pooling resources, knowledge, and expertise, will likely drive this monumental endeavor. Joint missions, shared research, and a unified vision can help overcome fiscal, technological, and logistical barriers, accelerating our lunar aspirations.
Moreover, an internationally-backed moonbase holds symbolic significance. It represents a beacon of human unity, collaboration, and shared exploration, transcending geopolitical boundaries.
Conclusion: A Glimpse into the Future
Considering the current technological landscape, the construction of a moonbase in the coming decades is not just plausible; it’s probable. Our growing understanding of the lunar environment, coupled with rapid advancements in relevant tech domains, sets the stage for an ambitious lunar project.
While challenges persist, the convergence of international efforts and the relentless spirit of human exploration promise a future where the moon becomes our next frontier, not just to visit, but to live and thrive.
