The use of robots in the field of medicine
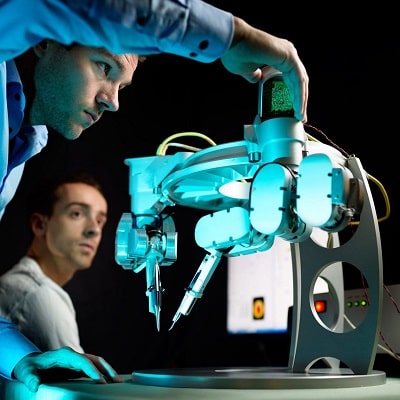
The use of robotics in medicine simplifies operations, reduces the purchase of consumables and allows medical staff to devote more time to patients.
Possibilities of robotics
Technologies such as robotic arms appeared in the field of medicine as early as the 1980s to assist during surgical interventions. Today, the capabilities of robots are being expanded in many other areas of healthcare through data analytics, computer vision, and artificial intelligence. And they are used not only for operations, but also for other purposes:
- during patient care;
- in research laboratories to automate bulky manual work;
- to move weights, beds or patients, reducing the physical burden on medical staff;
- for cleaning and preparation of wards in infectious diseases departments in order to limit contacts between people;
- robots with artificial intelligence software are used to distribute medicines in hospitals to patients.
These robots can keep track of the availability of medicines, equipment and supplies, place orders and keep track of inventory, alleviating shortages of staff.
Surgical care robots
Surgical robots help surgeons perform complex operations that require precision, speed and machine vision. Some robots equipped with artificial intelligence technologies can perform some tasks on their own, leaving the surgeons with only control over the procedures.

Robots perform surgical operations, which fall into two categories
- Operations on soft tissues. These robots are fixed in one position, penetrating through a small incision and creating conditions for the operation using remote control. This reduces the recovery time for the patient and the risk of infection or complications. Through a tiny incision, it is extremely difficult for a surgeon to make precise movements, which is why it is better to entrust this work to a robot.
- Orthopedic operations. AI simulation allows robots to be given precise instructions on how to perform orthopedic surgery procedures. To help the surgeon, these robots offer their data analysis, 3D visualization and intelligent manipulators. They can be programmed for hip or knee replacements.
In operating rooms equipped with surgical care robots, there is the possibility of video consultations with other specialists. Greater use of artificial intelligence enables surgical robots to:
- distinguish between different types of tissue in their field of view;
- avoid damage to muscles and nerves;
- provide the surgeon with complete information about the progress of the operation.
Robotics plays an important role in education as well. Virtually surgeons can practice operating the robot.
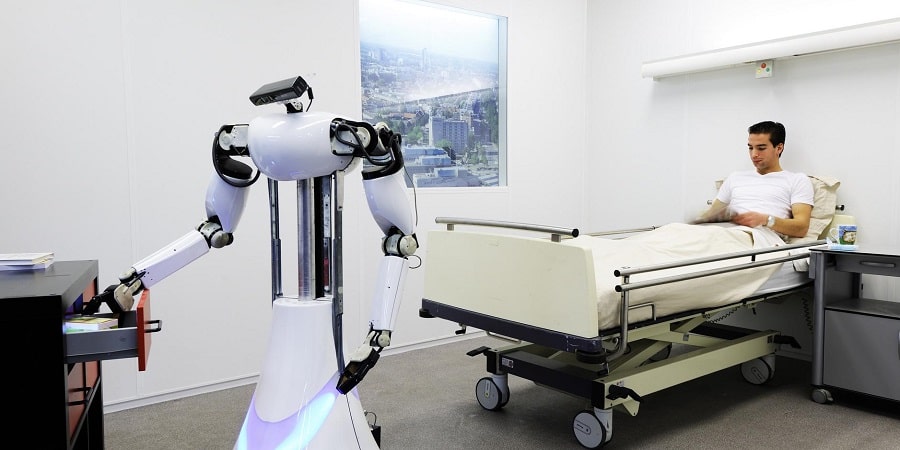
Other types of robots used in medicine
Other branches of medicine also cannot do without the help of robotics. The following devices perform different functions:
- therapeutic robots help patients with rehabilitation after traumatic brain injury, paralysis or stroke;
- Robotic wheelchair arms are being used for patients with spinal cord injuries;
- during procedures and exercises performed by patients, robots equipped with cameras and sensors take readings more accurately than the human eye;
- mobile robots equipped with distance measuring systems can accompany patients to rooms and procedures;
- service robots are involved in the transportation of linen to the laundry or equipment to the warehouse, the delivery of documentation to nurses and doctors.
Some types of robots help medical staff before seeing patients by recording blood oxygen levels and body temperature. Modern technologies for medical robots offer a wide range of devices with computer vision and highly sensitive sensors.
